Finding MAC, ethernet or hardware address
The media access control (MAC) address, also known as ethernet address or hardware address is supposed to uniquely identify a network interface. In Genetics it is used to configure your computer on the network. Some instructions to find what it is are below.
Windows XP or older
Windows XP (and older) is no longer permitted to be connected directly to the University network.
Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 & Windows 10
- Go to the start menu, search for cmd.exe and run it
- Enter the command getmac /fo list /v
C:\Users\Computer Officer>getmac /fo list /v
Connection Name: Local Area Connection
Network Adapter: Broadcom NetLink (TM) Fast Ethernet
Physical Address: 00-26-22-AA-BB-CC
Transport Name: \Device\Tcpip_{090B3FD8-28B1-47E0-82CD-B5C1FF7C3CE6}
Connection Name: Wireless Network Connection
Network Adapter: Intel(R) WiFi Link 5100 AGN
Physical Address: 00-1E-65-DD-EE-FF
Transport Name: Media disconnected
You're looking for the non-wireless one.
MacOS 10.4+
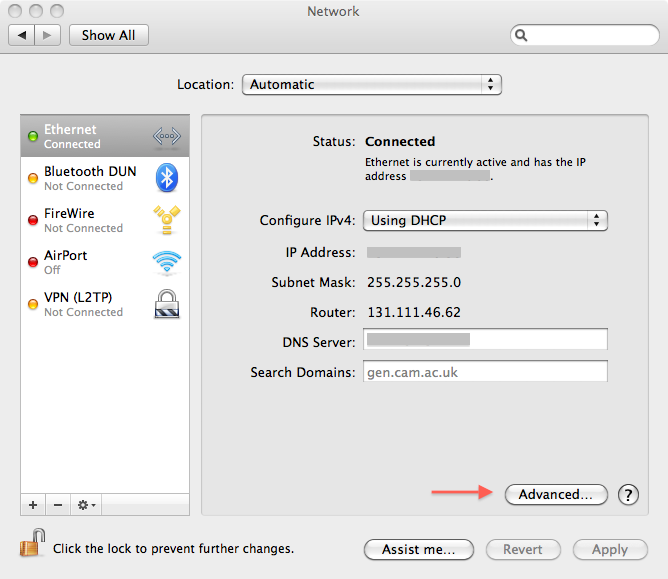
A video, or follow these steps. Open System Preferences, then Network. Select the appropriate connection then click advanced (shown by the red arrow.)
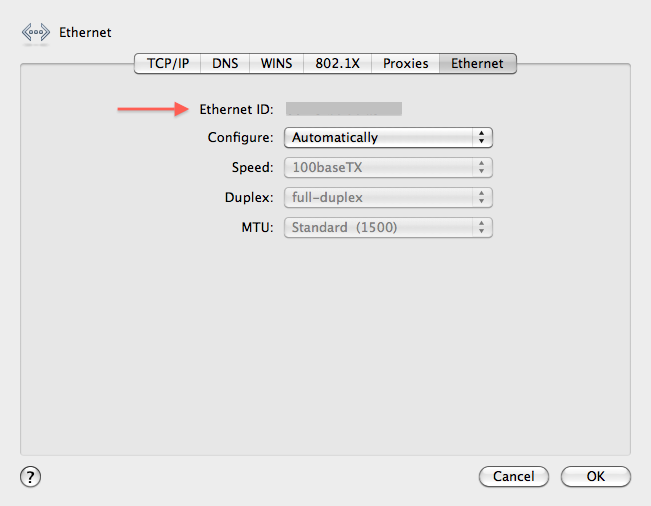
In the "ethernet" section of the advanced panel you can see the Ethernet ID aka MAC address.
Linux, Other UNIXes
- Open a terminal, eg: for Mac OS 10, Terminal, in Applications:Utilities, or Linux, xterm
- Type /sbin/ifconfig -a
- The information output is of the format:
network card: details - The field that matters is the one after "ether" or "HWaddr"
eg: (Mac OS)
en0: flags=8863<UP,BROADCAST,SMART,RUNNING,SIMPLEX,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet6 fe80::20a:95ff:fed2:bebc prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x4
inet 131.111.46.98 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 131.111.46.255
ether 00:0a:95:d2:be:bc
media: autoselect (100baseTX <full-duplex>) status: active
supported media: none autoselect 10baseT/UTP <half-duplex> 10baseT/UTP <full-duplex>
10baseT/UTP <full-duplex,hw-loopback> 100baseTX <half-duplex> 100baseTX <full-duplex>
100baseTX <full-duplex,hw-loopback> 1000baseTX <full-duplex> 1000baseTX <full-duplex,hw-loopback>
1000baseTX <full-duplex,flow-control> 1000baseTX <full-duplex,flow-control,hw-loopback>
eg: (Linux)
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:69:08:AB:DF
inet addr:131.111.46.212 Bcast:131.111.46.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:19819552 errors:7 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:6
TX packets:2399185 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:164
collisions:0 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:2453315455 (2.2 GiB) TX bytes:998436641 (952.1 MiB)
Interrupt:27
